This User Guide contains helpful hints to get you started and to answer your most common questions about our Pipeline Cloud integration.
Read an overview of Pipeline Cloud
The User Guide includes:
-
SQL Syntax Tips that will help you adapt your specific commands you’ve used with other databases to our platform
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Pipeline Cloud details
-
Best Practices for working with your database
-
Troubleshooting suggestions for common issues
For a more detailed look at the full list of available tables and fields as well our entity relationship diagrams for our database structure, be sure to also read our Developer Documentation.
Read the developer documentation
SQL Syntax Tips
You may be used to creating queries using MySQL but in Pipeline Cloud, you will need to create your queries using Microsoft SQL. While there are many similarities, there are a few key differences.
 Read the Microsoft Transact SQL Reference Guide
Read the Microsoft Transact SQL Reference Guide Read MsSqlTips - MySql to SQL Server Coding Differences
Read MsSqlTips - MySql to SQL Server Coding Differences Read a comparison between MySQL vs. MS SQL Server
Read a comparison between MySQL vs. MS SQL Server
Some common commands are the same in Microsoft SQL and MySQL, including:
-
Counting rows. Use COUNT().
-
Sorting rows. Use ORDER BY.
-
Unique rows. Use DISTINCT.
-
Renaming columns, also known as column aliases. All the variations below are equivalent.
SELECT co.FirstName AS 'FName' FROM Contacts co WHERE LastName = 'Jones'
SELECT co.FirstName AS FName FROM Contacts co WHERE LastName = 'Jones'
SELECT co.FirstName FName FROM Contacts co WHERE LastName = 'Jones'
There are also some standard queries from MySQL that you may want to use but that you will need to adapt to use with Pipeline Cloud. A few examples are listed below to help get you started.
- Joining tables (inner join, outer join, union join)
-
Formal join syntax is the same in MySQL and Microsoft SQL. However, MySQL allows for skipping the “ON <join condition>” when it can be inferred.
-
About the queries below:
-
Same: Equivalent tables, columns output, filter criteria.
-
Different: The MySQL join condition is absent.
-
Microsoft SQL example from Pipeline
SELECT co.VanID, co.FirstName, co.LastName, co.EmployerName, co.OccupationName
, ca.AddressLine1, ca.AddressLine2, ca.State, ca.ZipOrPostal
FROM Contacts co INNER JOIN dbo.ContactsAddresses ca ON co.VanID = ca.VanID
WHERE ca.DateCreated BETWEEN '1/1/2020' and '1/31/2020'
MySQL syntax example
SELECT co.cons_id, co.firstname, co.lastname, co.employer, co.occupation
, ca.addr1, ca.addr2, ca.city, ca.state_cd, ca.zip, ca.zip_4
, ca.create_dt
FROM cons co INNER JOIN cons_addr ca
where ca.create_dt BETWEEN '1/1/2020' and '1/31/2020'
- The first five in a list (Top 5)
-
The syntax difference here is Top N versus Limit N. The location of query hint is also different.
-
About the queries below:
-
Same: Equivalent tables, columns output.
-
Different: The MySQL syntax is LIMIT at the bottom of the query while Microsoft SQL uses TOP after the SELECT.
-
Microsoft SQL example from Pipeline
SELECT TOP 5 co.VanID, co.FirstName, co.LastName, co.EmployerName, co.OccupationName
FROM Contacts co
MySQL syntax example
SELECT co.cons_id, co.firstname, co.lastname, co.employer, co.occupation
FROM cons co
LIMIT 5
- Concatenation and Implicit Conversions of data types
-
The syntax difference here is that MySQL uses the CONCAT function while Microsoft SQL uses the plus sign. MySQL will also do implicit data conversions.
-
About the queries below:
-
Same: Equivalent tables, columns output.
-
Different: Usage of CONCAT versus the plus sign. Microsoft SQL requires the CONVERT function because the VanID is a number and must be converted to string data type when concatenated to strings.
-
Microsoft SQL example from Pipeline
SELECT co.firstname + co.lastname + CONVERT(VARCHAR(20),co.VanID)
FROM Contacts co
WHERE co.lastname = 'Smith' AND co.firstname IS NOT NULL
MySQL syntax example
SELECT CONCAT(co.firstname, co.lastname, co.cons_id)
FROM cons co
WHERE co.lastname = 'Smith' AND co.firstname IS NOT NULL
- Batch delimiters (GO and the semicolon)
-
Both systems allow for batch execution delimiters.
-
MySQL uses the semicolon but Microsoft SQL uses GO; (the semicolon is an optional statement delimiter).
Microsoft SQL example from Pipeline
SELECT co.FirstName FROM Contacts co WHERE LastName = 'Jones';
GO
SELECT co.LastName FROM Contacts co WHERE LastName = 'Jones'
GO
MySQL syntax example
SELECT co.firstname FROM cons co WHERE co.lastname = 'Jones';
SELECT co.lastname FROM cons co WHERE co.lastname = 'Jones';
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Pipeline Cloud
- Will deleted or suppressed records be in my cloud database?
Hard deleted transactions will be removed from the cloud database and soft deletes will not.
The following tables with soft deletes contain a column named DateSuppressed that you can use for WHERE clauses:
-
Contacts
-
Events
-
EventSignups
-
Address
- Will primary keys be in my cloud database?
Yes, Azure SQL Database enforces primary keys.
- How do I verify the database schema (Information Schema)?
You can use Azure SQL Database to query your database to verify the schema using Information Schema views. Full documentation is available.
 Read more on Information Schema Documentation
Read more on Information Schema Documentation
A few common queries include:
Tables in the database
SELECT TABLE_NAME, TABLE_TYPE, TABLE_SCHEMA
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
Column Names in tables
SELECT TABLE_CATALOG, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, COLUMN_NAME, COLUMN_DEFAULT
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
Key columns in tables
SELECT CONSTRAINT_NAME, TABLE_NAME, COLUMN_NAME, CONSTRAINT_SCHEMA, TABLE_SCHEMA
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.KEY_COLUMN_USAGE
- Does PowerBI work with my cloud database?
Yes, both the online and desktop versions support authentication with Azure Active Directory with MFA.
Important: Database name is required connection information.
PowerBI Desktop tips:
-
If you already have PowerBI desktop installed, verify that you have version 2.86.727.0 or higher.
-
When connecting to PowerBI for the first time from the Home ribbon select Get Data, select Azure SQL Database. Click Connect.
-
Enter connection information on the first screen that you will see:
-
Database name: <name of database in the invitation email>
-
Choose whether to Import data or to connect directly to your database
-
Select OK
-
On the next screen you will be asked to provide account information:
-
Authentication: Select “Microsoft account”.
-
Press the Sign In button to enter the multi-factor authentication workflow.
-
If you have already authenticated from the machine you are on, you will see your Microsoft account listed. Otherwise, select Use Another Account and provide the User name: <email address that received the invitation and created a cloud user account>
-
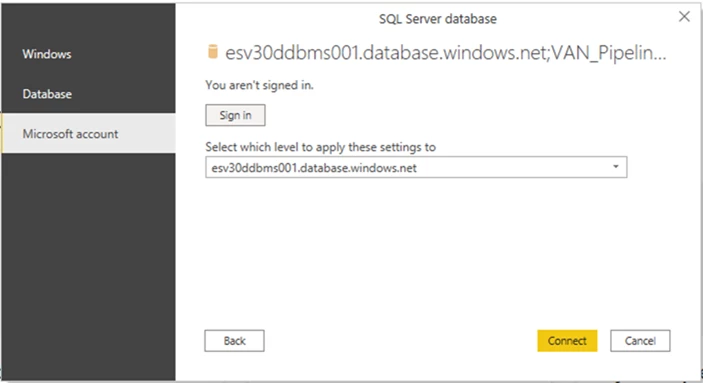
-
When connecting to PowerBI after initial setup, from the Home ribbon select Recent Sources.
-
You will need to reauthenticate using the Microsoft account option.
-
Best practices for querying your database
- Use the TOP query hint to limit results
-
Why? To prevent very long-running queries and slowness.
-
Alternatives: Increase the value from 100 to 1000 to 10000.
- Avoid using SELECT *
-
Why? To prevent very long-running queries and slowness.
-
Alternatives: Specify the column names.
- Avoid using CROSS JOIN
-
Why? Cross-joins produce a Cartesian product; this means many more rows and can be very long running queries. If you have 70,000 rows in Table1 and 90,000 rows in Table2, a CROSS JOIN will give you 6,300,000,000 rows.
-
Alternatives: No recommendation.
Troubleshooting
- What is the typical latency for Pipeline Cloud queries?
-
General latency ranges from ten to fifteen minutes. Contact Customer Support if latency exceeds one hour.
-
This product does not have any service level agreements.
- How do I handle Azure Data Studio connection errors?
-
If you already have Azure Data Studio installed, verify that you have version 15.02 or higher.
-
Database name is required connection information.
-
If you receive connection error Login failed for user <token-identified principal>, you must clear old connections:
-
Click on the person icon in the bottom left corner of Azure Data Studio. Any linked accounts will display.
-
Click the X to delete the old connection.
-
Click Yes on the confirmation modal.
-
-
Double-check your setup details.
-
If you are sure your setup is correct, refer to the Microsoft documentation for further help.
- How do I handle SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) connection errors?
-
If you already have SSMS installed, verify that you have version 18.6 or higher.
-
Database name is required connection information. This is on the Connection Properties tab when Options is clicked.
-
Double-check your setup details.
-
If you are sure your setup is correct, refer to the Microsoft documentation for further help.
- User account set up and missing invitation email
-
Check your spam folder and search for an email from Microsoft Invitations on behalf of EveryAction from invites@microsoft.com
Alternate search terms: Pipeline, Cloud, Azure SQL, User Guide, SQL Syntax, FAQ, Scratch, Save to my database, information schema, best practices

